C++ if Input Is Wrong Ask for Student 1 Again

Welcome! If you desire to acquire how to work with while loops in Python, then this article is for yous.
While loops are very powerful programming structures that you tin can apply in your programs to echo a sequence of statements.
In this article, y'all volition larn:
- What while loops are.
- What they are used for.
- When they should be used.
- How they piece of work backside the scenes.
- How to write a while loop in Python.
- What infinite loops are and how to interrupt them.
- What
while Truthfulis used for and its general syntax. - How to use a
intermissionstatement to stop a while loop.
You will acquire how while loops work backside the scenes with examples, tables, and diagrams.
Are you ready? Let'due south brainstorm. 🔅
🔹 Purpose and Utilise Cases for While Loops
Let'due south commencement with the purpose of while loops. What are they used for?
They are used to repeat a sequence of statements an unknown number of times. This type of loop runs while a given status is True and it only stops when the status becomes False.
When we write a while loop, we don't explicitly ascertain how many iterations will be completed, nosotros simply write the condition that has to be True to continue the process and Fake to stop it.
💡 Tip: if the while loop condition never evaluates to False, then we volition have an infinite loop, which is a loop that never stops (in theory) without external intervention.
These are some examples of real employ cases of while loops:
- User Input: When we inquire for user input, we demand to bank check if the value entered is valid. We tin can't possibly know in accelerate how many times the user will enter an invalid input earlier the programme tin can continue. Therefore, a while loop would be perfect for this scenario.
- Search: searching for an element in a data construction is another perfect use case for a while loop because we can't know in advance how many iterations will be needed to find the target value. For instance, the Binary Search algorithm tin be implemented using a while loop.
- Games: In a game, a while loop could exist used to continue the main logic of the game running until the player loses or the game ends. Nosotros tin't know in advance when this will happen, so this is another perfect scenario for a while loop.
🔸 How While Loops Work
Now that you know what while loops are used for, let'southward run into their main logic and how they work behind the scenes. Hither we have a diagram:

Let's interruption this downwardly in more detail:
- The process starts when a while loop is found during the execution of the program.
- The condition is evaluated to cheque if it's
TrueorFake. - If the status is
True, the statements that belong to the loop are executed. - The while loop condition is checked once again.
- If the condition evaluates to
Trueagain, the sequence of statements runs again and the process is repeated. - When the status evaluates to
Fake, the loop stops and the programme continues beyond the loop.
One of the about of import characteristics of while loops is that the variables used in the loop condition are not updated automatically. We have to update their values explicitly with our code to make sure that the loop will eventually stop when the condition evaluates to Simulated.
🔹 General Syntax of While Loops
Great. Now you know how while loops work, so let's swoop into the code and meet how you tin write a while loop in Python. This is the basic syntax:
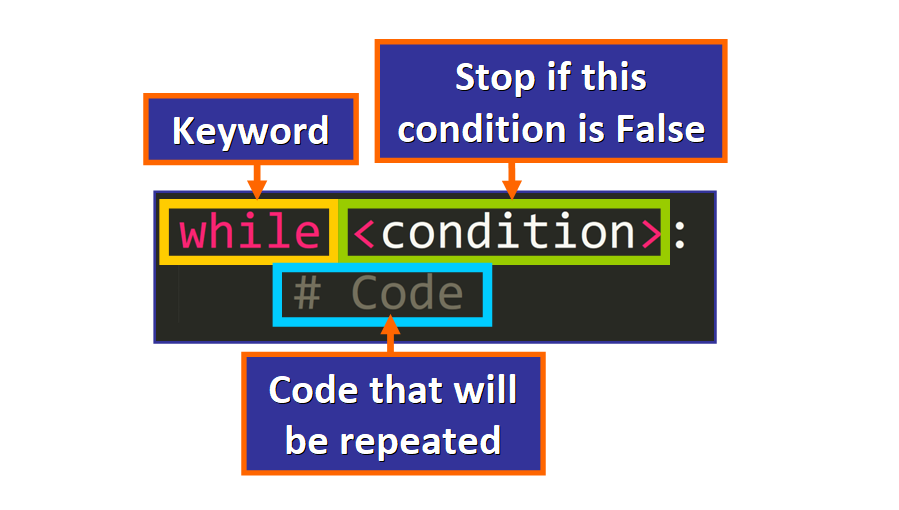
These are the main elements (in social club):
- The
whilekeyword (followed by a space). - A status to decide if the loop volition continue running or not based on its truth value (
TrueorImitation). - A colon (
:) at the end of the first line. - The sequence of statements that volition be repeated. This block of code is chosen the "torso" of the loop and it has to be indented. If a argument is not indented, it will not be considered part of the loop (please see the diagram below).
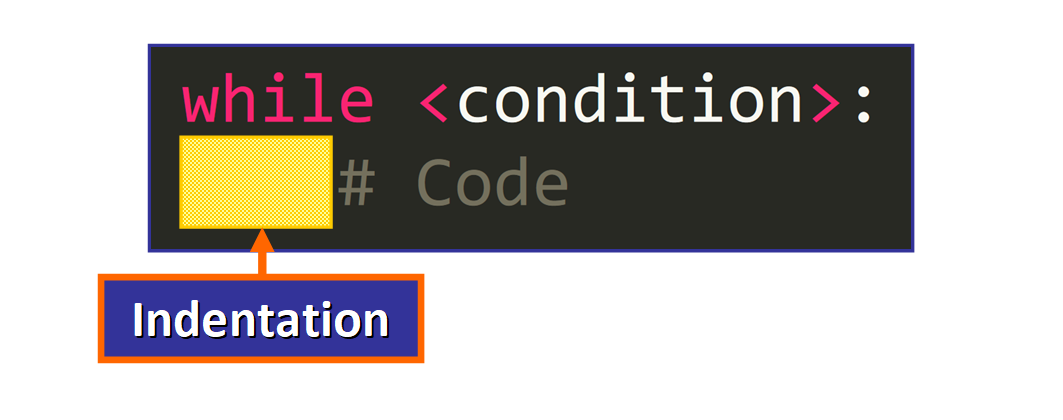
💡 Tip: The Python way guide (PEP viii) recommends using iv spaces per indentation level. Tabs should merely be used to remain consequent with lawmaking that is already indented with tabs.
🔸 Examples of While Loops
Now that y'all know how while loops work and how to write them in Python, let's see how they work behind the scenes with some examples.
How a Basic While Loop Works
Hither we have a basic while loop that prints the value of i while i is less than eight (i < 8):
i = 4 while i < 8: print(i) i += 1 If nosotros run the lawmaking, we see this output:
four 5 6 7 Let'southward encounter what happens behind the scenes when the code runs:
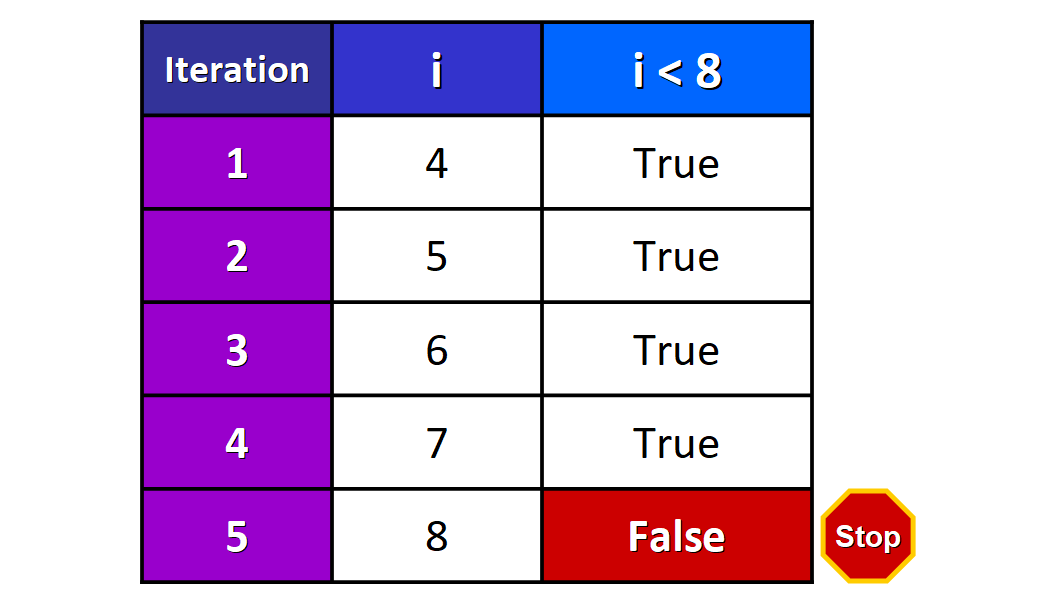
- Iteration ane: initially, the value of
iis 4, so the conditioni < viiievaluates toTrueand the loop starts to run. The value ofiis printed (four) and this value is incremented past ane. The loop starts again. - Iteration two: now the value of
iis v, and then the conditioni < viiievaluates toTrue. The torso of the loop runs, the value ofiis printed (v) and this valueiis incremented by 1. The loop starts again. - Iterations three and 4: The same process is repeated for the third and fourth iterations, and then the integers 6 and vii are printed.
- Earlier starting the fifth iteration, the value of
iis8. Now the while loop conditioni < 8evaluates toFalseand the loop stops immediately.
💡 Tip: If the while loop condition is False before starting the get-go iteration, the while loop volition not even starting time running.
User Input Using a While Loop
Now let'south run across an instance of a while loop in a program that takes user input. We volition the input() function to enquire the user to enter an integer and that integer will only be appended to list if it'south even.
This is the code:
# Define the list nums = [] # The loop will run while the length of the # list nums is less than 4 while len(nums) < four: # Ask for user input and store information technology in a variable as an integer. user_input = int(input("Enter an integer: ")) # If the input is an even number, add it to the list if user_input % two == 0: nums.append(user_input) The loop condition is len(nums) < iv, so the loop will run while the length of the list nums is strictly less than 4.
Let's analyze this program line by line:
- We start by defining an empty list and assigning it to a variable called
nums.
nums = [] - Then, we define a while loop that will run while
len(nums) < iv.
while len(nums) < 4: - Nosotros ask for user input with the
input()role and store it in theuser_inputvariable.
user_input = int(input("Enter an integer: ")) 💡 Tip: We need to catechumen (cast) the value entered by the user to an integer using the int() function before assigning it to the variable because the input() function returns a string (source).
- We cheque if this value is fifty-fifty or odd.
if user_input % 2 == 0: - If information technology's even, nosotros append information technology to the
numslist.
nums.append(user_input) - Else, if information technology's odd, the loop starts once again and the condition is checked to determine if the loop should keep or non.
If nosotros run this code with custom user input, we get the following output:
Enter an integer: iii Enter an integer: four Enter an integer: two Enter an integer: 1 Enter an integer: vii Enter an integer: vi Enter an integer: iii Enter an integer: 4 This table summarizes what happens backside the scenes when the code runs:
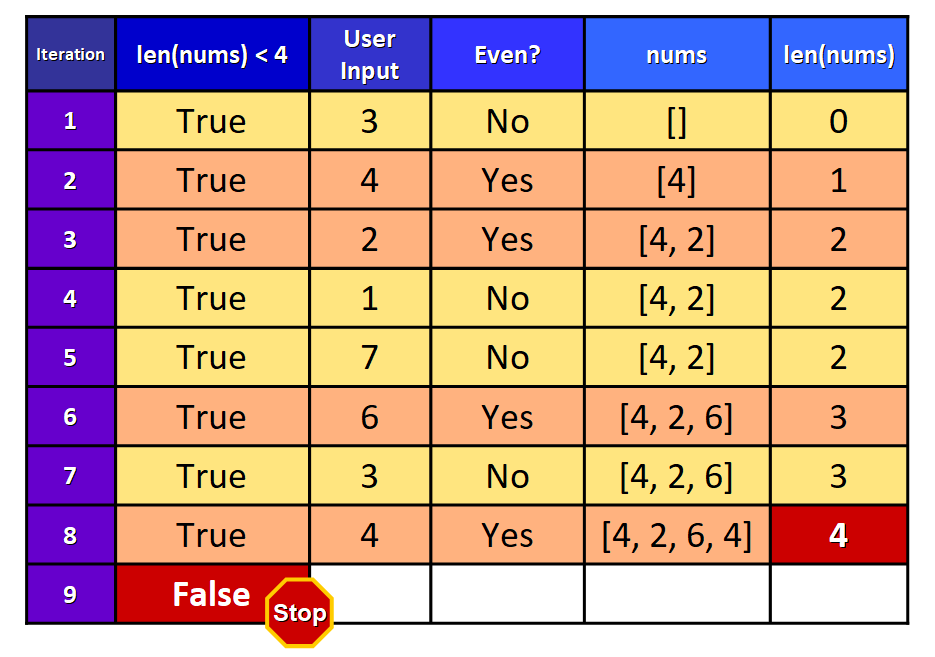
💡 Tip: The initial value of len(nums) is 0 because the list is initially empty. The last column of the table shows the length of the list at the end of the current iteration. This value is used to bank check the condition earlier the next iteration starts.
As yous can run into in the table, the user enters even integers in the 2nd, third, sixth, and eight iterations and these values are appended to the nums list.
Before a "9th" iteration starts, the status is checked once again but now information technology evaluates to Imitation because the nums listing has four elements (length 4), so the loop stops.
If nosotros check the value of the nums list when the process has been completed, we see this:
>>> nums [four, 2, 6, 4] Exactly what we expected, the while loop stopped when the condition len(nums) < 4 evaluated to False.
At present you lot know how while loops piece of work behind the scenes and you've seen some applied examples, so allow's swoop into a key chemical element of while loops: the status.
🔹 Tips for the Condition in While Loops
Earlier yous start working with while loops, yous should know that the loop condition plays a central role in the functionality and output of a while loop.
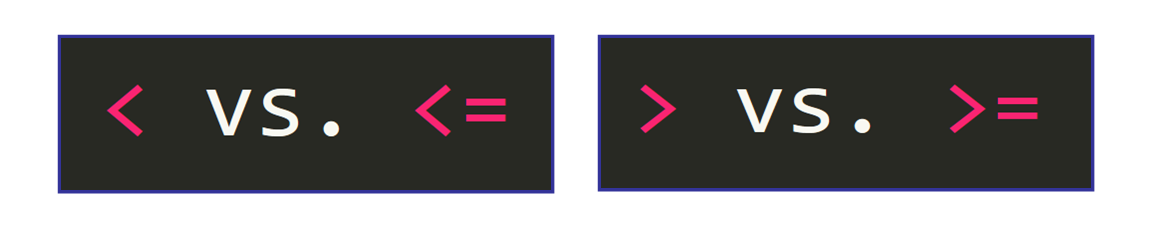
You must be very conscientious with the comparison operator that you choose considering this is a very common source of bugs.
For example, common errors include:
- Using
<(less than) instead of<=(less than or equal to) (or vice versa). - Using
>(greater than) instead of>=(greater than or equal to) (or vice versa).
This can bear on the number of iterations of the loop and even its output.
Allow's see an instance:
If nosotros write this while loop with the condition i < nine:
i = 6 while i < 9: impress(i) i += 1 We see this output when the code runs:
6 7 8 The loop completes three iterations and it stops when i is equal to ix.
This table illustrates what happens behind the scenes when the code runs:
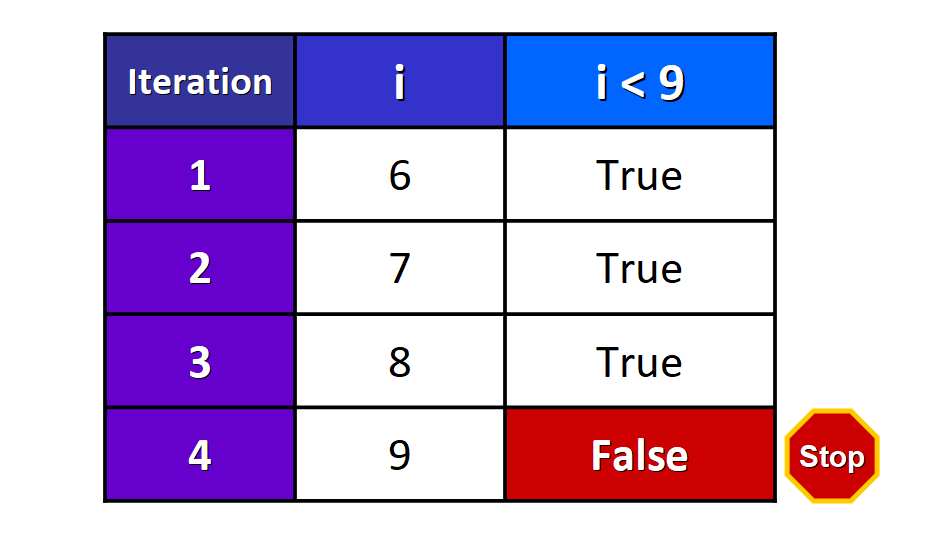
- Earlier the starting time iteration of the loop, the value of
iis 6, then the conditioni < 9isTruthfuland the loop starts running. The value ofiis printed and so it is incremented past ane. - In the second iteration of the loop, the value of
iis 7, so the conditioni < nineisTrue. The body of the loop runs, the value ofiis printed, and so it is incremented past 1. - In the tertiary iteration of the loop, the value of
iis 8, so the conditioni < 9isTruthful. The torso of the loop runs, the value ofiis printed, and then it is incremented by ane. - The condition is checked again before a fourth iteration starts, merely now the value of
iis 9, soi < nineisFalseand the loop stops.
In this instance, we used < as the comparing operator in the condition, but what do you retrieve will happen if nosotros use <= instead?
i = vi while i <= 9: print(i) i += one Nosotros run into this output:
6 7 viii 9 The loop completes one more iteration considering now we are using the "less than or equal to" operator <= , so the condition is still True when i is equal to 9.
This table illustrates what happens behind the scenes:
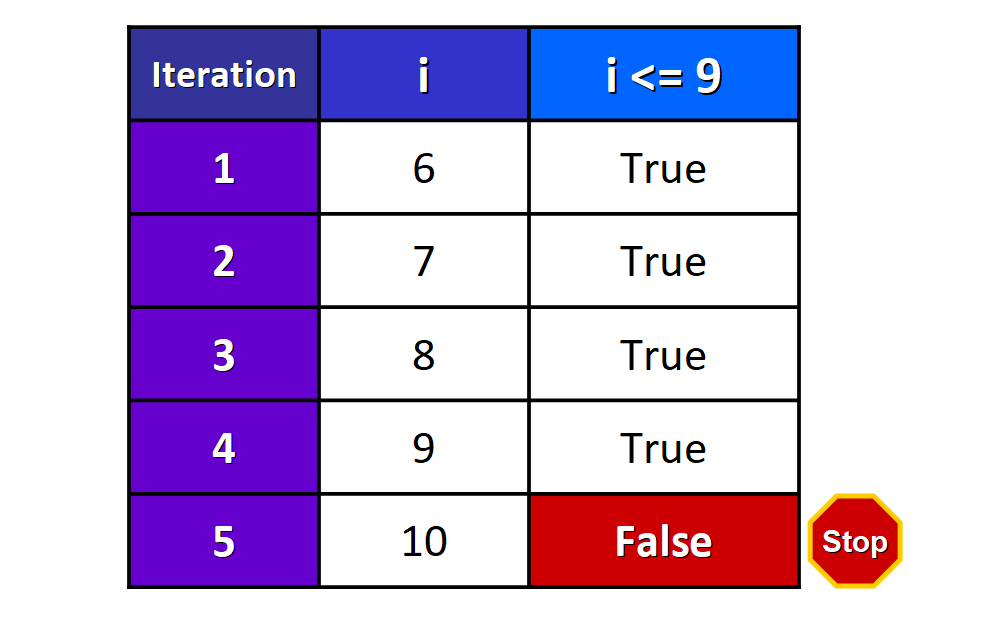
Four iterations are completed. The condition is checked again before starting a "fifth" iteration. At this point, the value of i is x, and then the status i <= 9 is Faux and the loop stops.
🔸 Infinite While Loops
Now y'all know how while loops work, simply what do you recollect will happen if the while loop condition never evaluates to Imitation?
What are Space While Loops?
Remember that while loops don't update variables automatically (we are in accuse of doing that explicitly with our lawmaking). And then there is no guarantee that the loop will stop unless nosotros write the necessary code to make the status False at some signal during the execution of the loop.
If we don't exercise this and the condition always evaluates to True, then we will have an infinite loop, which is a while loop that runs indefinitely (in theory).
Infinite loops are typically the upshot of a problems, only they can also be caused intentionally when nosotros want to repeat a sequence of statements indefinitely until a break statement is found.
Let'due south see these two types of infinite loops in the examples below.
💡 Tip: A bug is an error in the program that causes incorrect or unexpected results.
Example of Infinite Loop
This is an example of an unintentional infinite loop caused past a bug in the program:
# Define a variable i = v # Run this loop while i is less than 15 while i < 15: # Print a message impress("Hello, Globe!") Analyze this lawmaking for a moment.
Don't you find something missing in the torso of the loop?
That's right!
The value of the variable i is never updated (it's e'er 5). Therefore, the condition i < 15 is always True and the loop never stops.
If we run this lawmaking, the output will be an "infinite" sequence of Hello, World! letters because the body of the loop print("Hello, World!") will run indefinitely.
Hello, World! Hello, World! Hello, World! Hullo, World! Hello, World! Hello, Globe! Hello, World! Hello, World! Hello, World! Howdy, Earth! Hello, World! Hello, World! How-do-you-do, World! Hello, World! How-do-you-do, Globe! Howdy, World! Hello, Earth! Hullo, Earth! . . . # Continues indefinitely To cease the program, we will demand to interrupt the loop manually by pressing CTRL + C.
When we practice, we volition meet a KeyboardInterrupt error similar to this one:

To fix this loop, we will need to update the value of i in the torso of the loop to make sure that the status i < 15 will eventually evaluate to False.
This is one possible solution, incrementing the value of i by 2 on every iteration:
i = five while i < xv: print("Hullo, Globe!") # Update the value of i i += 2 Great. Now you know how to fix infinite loops caused by a issues. You but need to write code to guarantee that the condition will eventually evaluate to Simulated.
Let's start diving into intentional infinite loops and how they work.
🔹 How to Make an Space Loop with While True
We can generate an infinite loop intentionally using while True. In this case, the loop will run indefinitely until the procedure is stopped by external intervention (CTRL + C) or when a intermission statement is found (you volition learn more about break in just a moment).
This is the bones syntax:
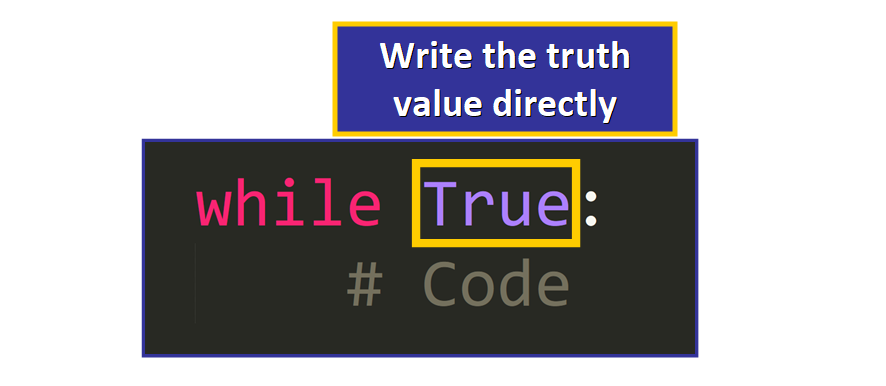
Instead of writing a status after the while keyword, nosotros just write the truth value directly to bespeak that the condition will e'er be True.
Here we take an example:
>>> while True: impress(0) 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 Traceback (most contempo phone call final): File "<pyshell#2>", line two, in <module> impress(0) KeyboardInterrupt The loop runs until CTRL + C is pressed, but Python also has a break statement that we tin can use directly in our code to end this type of loop.
The intermission argument
This statement is used to finish a loop immediately. Y'all should retrieve of it equally a red "stop sign" that you can use in your code to have more control over the behavior of the loop.

According to the Python Documentation:
Thesuspensionstatement, like in C, breaks out of the innermost enclosingfororwhileloop.
This diagram illustrates the basic logic of the break argument:
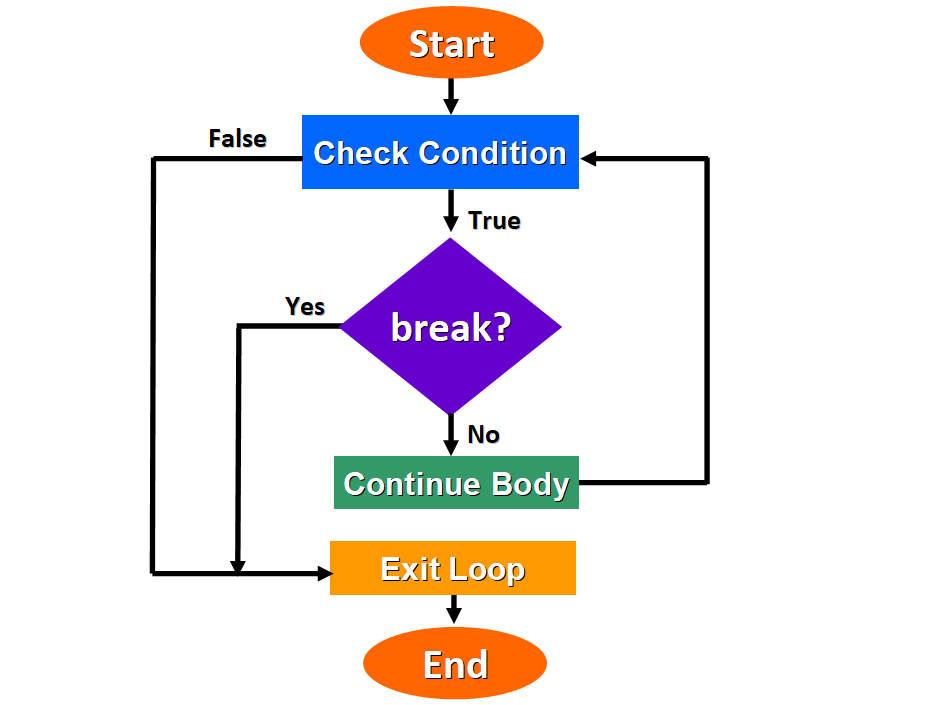
break argument This is the basic logic of the break statement:
- The while loop starts only if the condition evaluates to
True. - If a
breakstatement is found at whatsoever point during the execution of the loop, the loop stops immediately. - Else, if
pauseis not found, the loop continues its normal execution and it stops when the condition evaluates toFalse.
Nosotros can use break to cease a while loop when a condition is met at a particular point of its execution, so you will typically find it within a conditional argument, like this:
while True: # Code if <condition>: break # Lawmaking This stops the loop immediately if the condition is Truthful.
💡 Tip: You can (in theory) write a interruption statement anywhere in the body of the loop. It doesn't necessarily accept to be part of a conditional, but we commonly use it to stop the loop when a given condition is True.
Here we accept an case of suspension in a while Truthful loop:

Let's come across it in more particular:
The kickoff line defines a while True loop that will run indefinitely until a suspension argument is found (or until information technology is interrupted with CTRL + C).
while True: The second line asks for user input. This input is converted to an integer and assigned to the variable user_input.
user_input = int(input("Enter an integer: ")) The third line checks if the input is odd.
if user_input % 2 != 0: If information technology is, the bulletin This number is odd is printed and the break argument stops the loop immediately.
impress("This number of odd") break Else, if the input is even , the message This number is fifty-fifty is printed and the loop starts again.
print("This number is fifty-fifty") The loop will run indefinitely until an odd integer is entered considering that is the only way in which the break statement will exist found.
Here we accept an example with custom user input:
Enter an integer: 4 This number is even Enter an integer: 6 This number is even Enter an integer: 8 This number is even Enter an integer: 3 This number is odd >>> 🔸 In Summary
- While loops are programming structures used to repeat a sequence of statements while a condition is
True. They cease when the condition evaluates toFaux. - When you write a while loop, you lot demand to make the necessary updates in your code to make certain that the loop will somewhen stop.
- An space loop is a loop that runs indefinitely and it simply stops with external intervention or when a
breakstatement is plant. - You can stop an infinite loop with
CTRL + C. - Y'all can generate an infinite loop intentionally with
while True. - The
breakstatement tin exist used to stop a while loop immediately.
I really hope you liked my article and found it helpful. At present you know how to work with While Loops in Python.
Follow me on Twitter @EstefaniaCassN and if you want to acquire more most this topic, cheque out my online course Python Loops and Looping Techniques: Beginner to Advanced.
Learn to code for complimentary. freeCodeCamp's open source curriculum has helped more 40,000 people get jobs as developers. Get started
Source: https://www.freecodecamp.org/news/python-while-loop-tutorial/
0 Response to "C++ if Input Is Wrong Ask for Student 1 Again"
Enregistrer un commentaire